introduction to reactions
What causes particles to react?
For the particle to react there must be:
- A collision between two particles
- Correct orientation of the particles
- High enough kinetic energy of these particles
What is rate of reaction?
This is the speed in which the reactants are used up in the reaction. It measure frequency of reactions; the higher the frequency the higher the rate.
Units:
What Affects rate of reaction?
- Surface area - Linear
- Concentration - Linear
- Temperature - Quadratic
- Pressure - Linear
- Catalysts - Linear
How does surface area affect rate?
- Higher surface area means more particles are exposed
- This allows for a higher frequency of collisions.
- Leading to a higher rate of reactions.

How does concentration affect rate?
- Higher concentration means particles are closer together
- Particles more likely to collide.
- High frequency of collisions and hence rate of reaction
How does Temperature affect rate?
- Temperature is measure of kinetic energy so particles move with more speed
- Particles collide more frequently
- Particles collide with more strength
- Rate increases with temperature, in a quadratic manner.
How does pressure affect rate?
- Higher pressure means volume is smaller
- Particles are closer together
- Particles more likely to collide.
- High frequency of collisions and hence rate of reaction
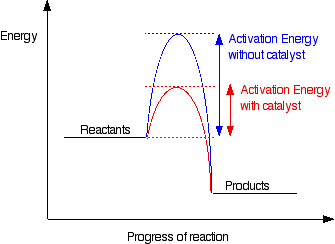
How do catalysts affect rate?
- Catalysts lower the activation energy of the reaction
- The energy required for a collision to cause a reaction is lower.
- More collisions cause reactions so frequency of reactions increases.
View count: 7584